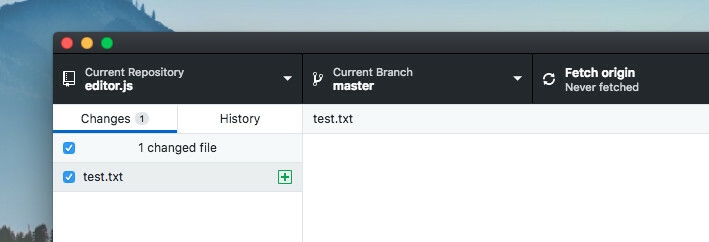
List of useful commands to work with submodules.
Add submodule
git submodule add https://github.com/*user*/*repo* path/to/submodule/directory
For using private repository as a submodule:
git submodule add git@github.com:*user*/*repo*.git path/to/submodule/directory
Example
git submodule add https://github.com/codex-team/editor.js editorjs
You will see changes in .gitmodules file and submodule's directory. Commit changes in both files.
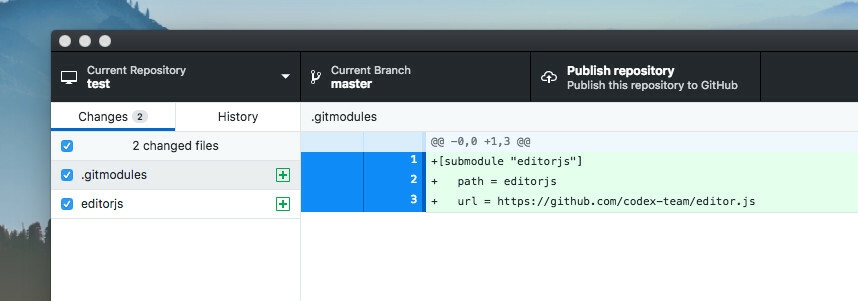
Init submodules
After cloning a repository with submodules you need to initialize them. Otherwise you will see empty directories in submodules places.
Git will download submodules recursively.
git submodule update --init --recursive
Pull updates
Pull submodules by commited state.
git submodule update --recursive
Get the latest updates for remote branches
git submodule update --recursive --remote
Remove submodule
1. Delete the relevant section from the .gitmodules file.
-[submodule "editorjs"]
- path = editorjs
- url = https://github.com/codex-team/editor.js
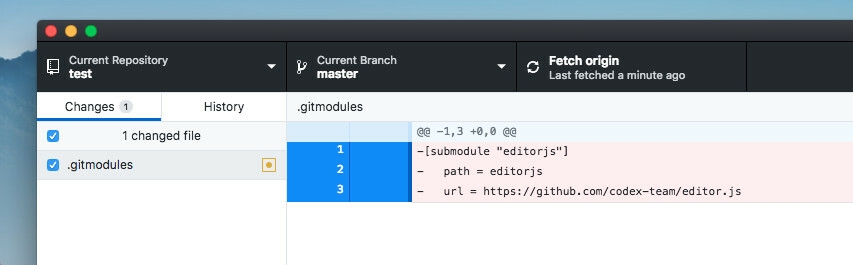
2. Stage the .gitmodules changes: git add .gitmodules.
3. Delete the relevant section from .git/config.
[core]
repositoryformatversion = 0
filemode = true
bare = false
logallrefupdates = true
ignorecase = true
precomposeunicode = true
[remote "origin"]
url = https://github.com/talyguryn/test
fetch = +refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/origin/*
[branch "master"]
remote = origin
merge = refs/heads/master
-[submodule "editorjs"]
- active = true
- url = https://github.com/codex-team/editor.js
4. Run git rm --cached path_to_submodule (no trailing slash).
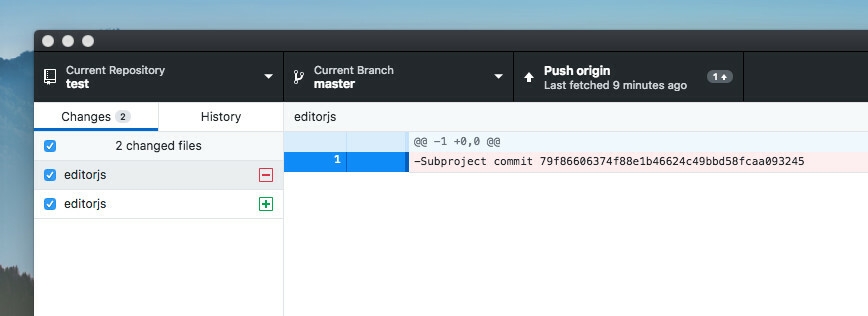
5. Run rm -rf .git/modules/path_to_submodule (no trailing slash).
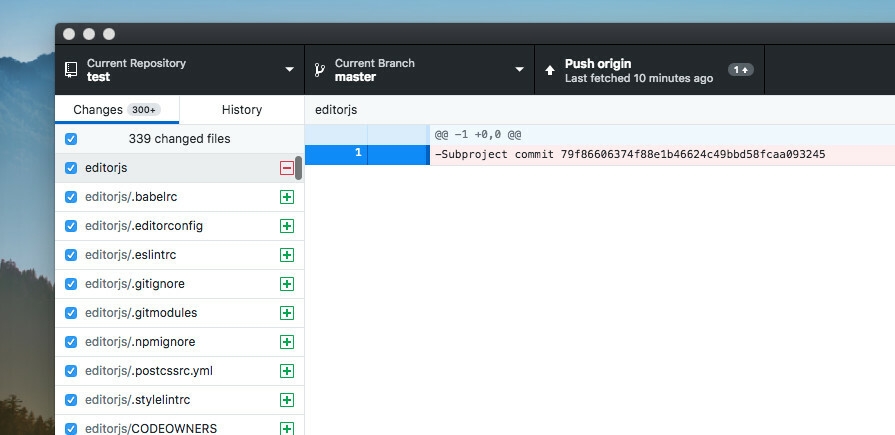
6. Delete the now untracked submodule files rm -rf path_to_submodule.
7. Commit changes: git commit -am "Remove submodule".
Working with submodules
You can work with any submodule via your git client (as a regular repository).
For example. Any changes inside submodule will be shown as dirty state.
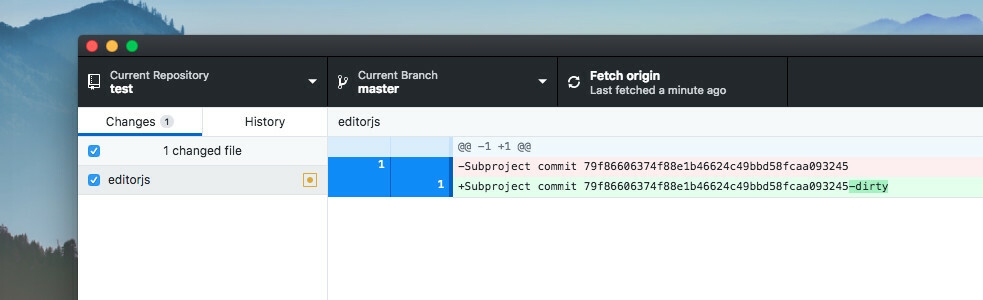
Add submodule's directory as a local repository.
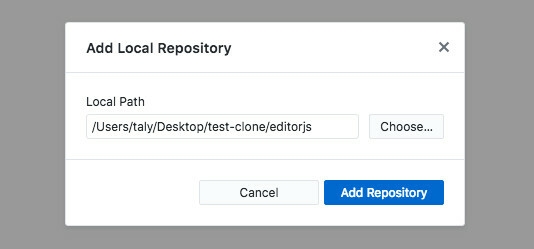
And you will see changes, commit them and checkout branches.