Request body data will be placed to req.body. A few examples for decoding popular request data formats:
application/x-www-form-urlencodedapplication/jsonmultipart/form-data
Form URL Encoded
application/x-www-form-urlencoded is a default data format for sending forms:
<form method="POST" action="/">
<input type="text" name="username" placeholder="username">
<input type="submit">
</form>
Use express.urlencoded middleware:
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
/** Decode Form URL Encoded data */
app.use(express.urlencoded());
/** Show page with a form */
app.get('/', (req, res, next) => {
res.send(`<form method="POST" action="/">
<input type="text" name="username" placeholder="username">
<input type="submit">
</form>`);
});
/** Process POST request */
app.post('/', function (req, res, next) {
res.send(JSON.stringify(req.body));
});
/** Run the app */
app.listen(3000);
Run this code and open localhost:3000.
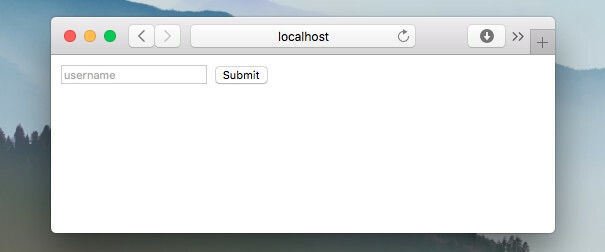
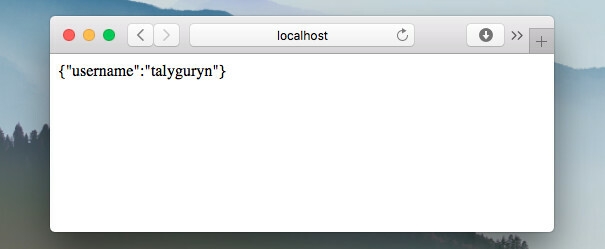
Fill the form and send. You will see a response:
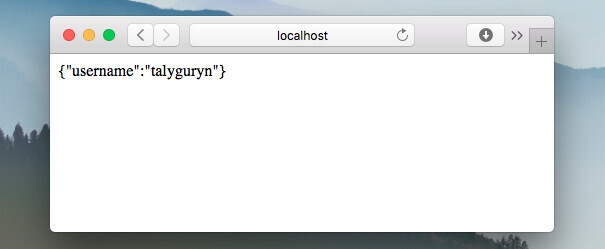
JSON
application/json mostly used for AJAX (XMLHttpRequest) requests.
Use express.json:
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
/** Decode JSON data */
app.use(express.json());
/** Show page with a input field, button and javascript */
app.get('/', (req, res, next) => {
res.send(`<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@codexteam/ajax"></script>
<script>
var send = function() {
var username = document.getElementById('username').value;
ajax.post({
url: '/',
data: {
username: username
},
})
.then(response => {
console.log(response.body)
})
.catch(console.error);
}
</script>
<input type="text" name="username" placeholder="username" id="username">
<button onclick="send()">Send</button>`);
});
/** Process POST request */
app.post('/', function (req, res, next) {
res.send(JSON.stringify(req.body));
});
/** Run the app */
app.listen(3000);
Run this code, open localhost:3000 and toggle web console.
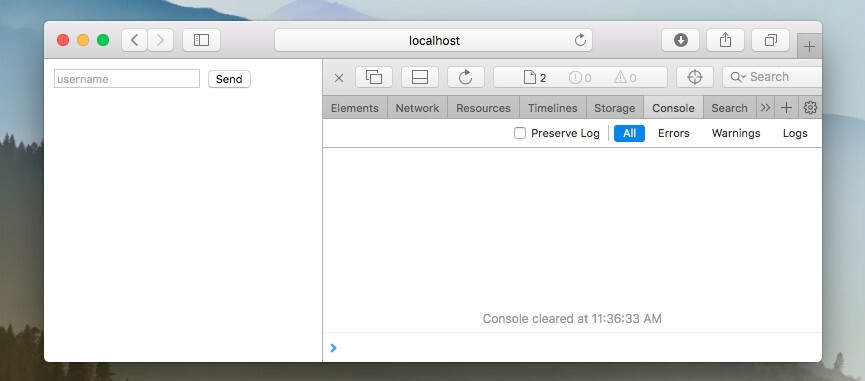
Fill the form and send it. In the console you will see a server response with data you have sent.
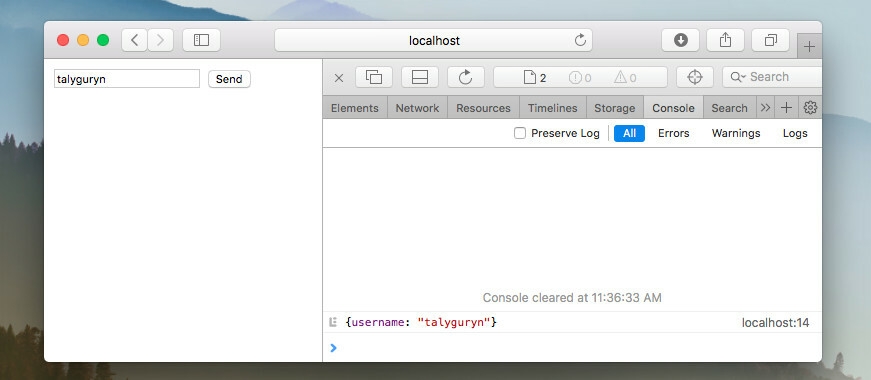
Form data
multipart/form-data used for sending files or form-data objects.
Express by default has no ability to parse this type of encoding. So you can use multer's middlewares.
For example try multer().none() middleware for decoding text-only multipart form.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
/** Require multer */
const multer = require('multer');
/** Show page with a form with a specific enctype */
app.get('/', (req, res, next) => {
res.send(`<form method="POST" action="/" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="text" name="username" placeholder="username">
<input type="submit">
</form>`);
});
/** Process POST request with a mutter's middleware */
app.post('/', multer().none(), function (req, res, next) {
res.send(JSON.stringify(req.body));
});
/** Run the app */
app.listen(3000);
Example page looks the same as a first one.
Run this code and open localhost:3000.
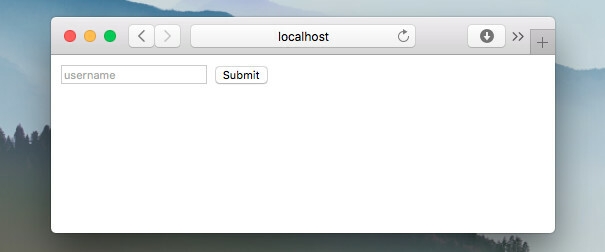
Fill the form and send. You will see a response:
For files uploading you read «Usage» section in multer's docs. Files data will be places to req.files.
